Cubiq introduces a revolutionary modular architecture that separates computation, validation, and consensus, enabling mobile devices to participate as first-class citizens in blockchain networks.
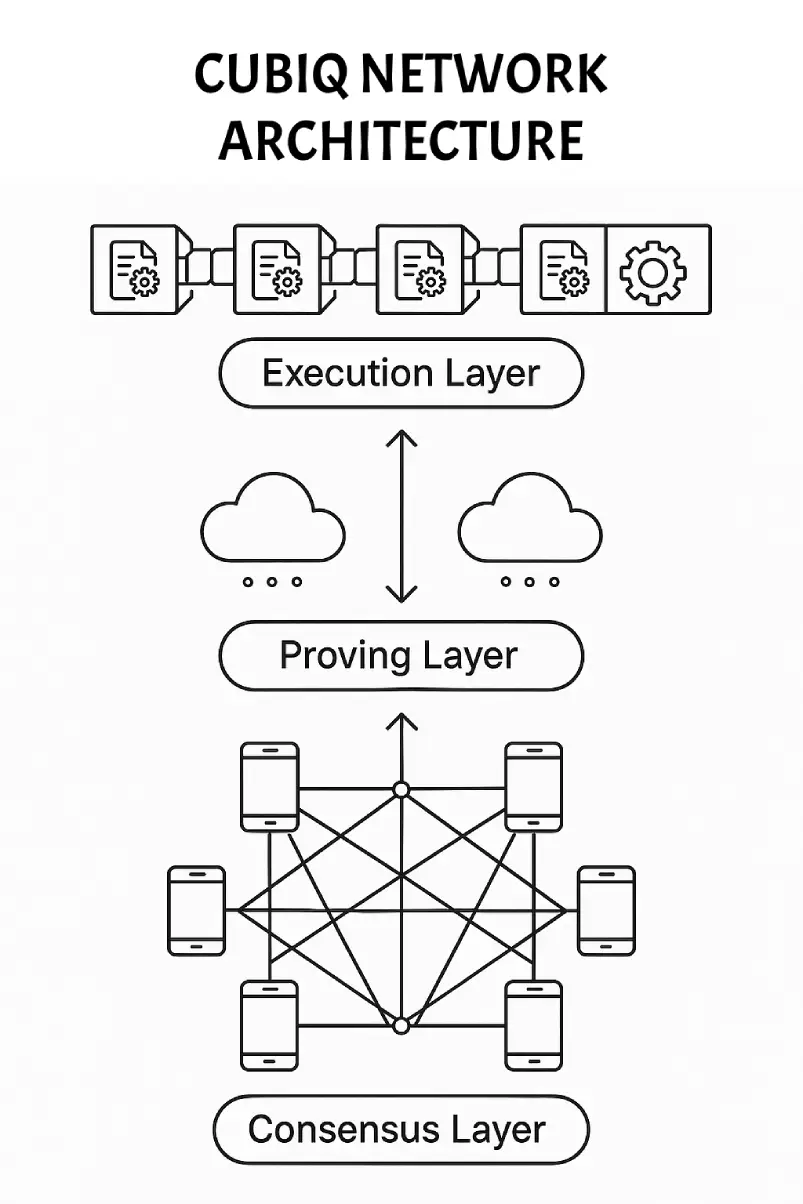
Cubiq's architecture consists of three primary layers that work together to enable mobile-native blockchain participation while maintaining security and decentralization.
EVM-compatible runtime environment supporting Solidity smart contracts with modifications for ZK constraint compatibility.
Based on Plonky3, this layer handles proof generation in a cloud-based prover network, enabling scalable zero-knowledge computation.
Lightweight Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus managed by mobile-based validators ("Qubes") with gossip-based P2P networking.
Cubiq is guided by five core principles that shape every architectural decision:
Every component is verifiable through cryptographic proofs. No black boxes or trusted intermediaries.
Designed to work on low-end Android and iOS phones with limited resources.
Pluggable consensus, proof systems, and APIs allow independent evolution of components.
All offloaded computation is verifiable through zero-knowledge proofs.
Qubes are lightweight mobile nodes that form the backbone of Cubiq's decentralized network. Each Qube performs several critical functions:
The Cloud Prover Network handles computationally intensive zero-knowledge proof generation:
The execution layer provides full EVM compatibility while being optimized for zero-knowledge proof generation:
Smart contracts on Cubiq execute in a modified EVM environment:
// Example: ZK-compatible smart contract
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract CubiqVoting {
mapping(address => bool) public hasVoted;
mapping(uint256 => uint256) public votes;
// ZK-friendly: simple state transitions
function vote(uint256 proposalId, bool support) external {
require(!hasVoted[msg.sender], "Already voted");
hasVoted[msg.sender] = true;
votes[proposalId] += support ? 1 : 0;
emit VoteCast(msg.sender, proposalId, support);
}
event VoteCast(address voter, uint256 proposalId, bool support);
}The proving layer is responsible for generating zero-knowledge proofs that validate state transitions:
Cubiq uses a lightweight Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus optimized for mobile participation:
The zkURL protocol is Cubiq's innovation for decentralized proof distribution:
zk://[proverID]@[domain_or_hash]/[proof_id]#[metadata]Example:
zk://prover01@prover.cubiq.org/block/8472934#v1Understanding how proofs flow through the system:
User submits transaction to mempool
Qube validator bundles transactions into block
Cloud prover generates zkProof using Plonky3
Proof published to zkURL endpoint for distribution
Mobile Qubes fetch and verify proof locally
2/3+ Qubes vote to finalize block
The Cloud Prover Network is designed for scalability, reliability, and decentralization:
| Layer | Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Layer | Rust zkEVM emulator | Transaction simulation |
| Circuit Layer | Plonky3 custom circuits | Proof generation |
| Compute Layer | GPU-accelerated instances | Parallel proving |
| Storage Layer | IPFS / Arweave / CDN | Proof distribution |
Cubiq's architecture is designed to scale to billions of mobile participants:
Theoretical maximum with parallel proving
Block time with instant finality
Potential mobile device participants
Cubiq's modular design enables continuous evolution without breaking changes:
The architecture described here represents the foundation of Cubiq Network. As the ecosystem grows, new components and optimizations will be added while maintaining backward compatibility and the core principle of mobile-native participation.